A yard of rock will typically cover an area of approximately 100 square feet when spread at a depth of 2 inches. This guide will help you with calculating rock volume and understanding rock coverage area for your landscaping projects, answering the common question of how much gravel do I need.
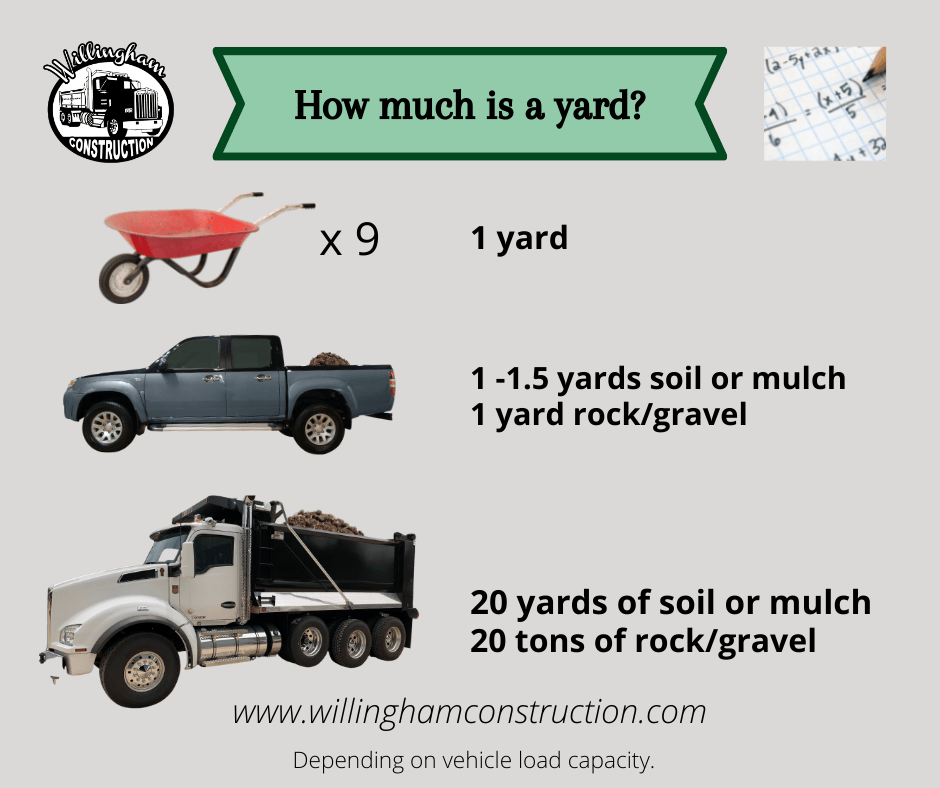
Image Source: lirp.cdn-website.com
Deciphering Rock Coverage: The Fundamentals
When embarking on a landscaping project that involves decorative rocks, gravel, or crushed stone, a crucial question arises: “How much rock do I need?” The answer hinges on several key factors, primarily the desired depth of coverage and the type of rock you select. Understanding these elements allows for accurate rock calculations for landscaping, ensuring you purchase the right amount and avoid costly overages or frustrating shortages. This guide will demystify the process of determining your rock yard coverage calculator needs.
The Magic Number: 100 Square Feet at 2 Inches
The generally accepted rule of thumb for cubic yard rock coverage is that one cubic yard of rock will cover approximately 100 square feet to a depth of 2 inches. This is a handy starting point, but it’s essential to delve deeper to account for variations in rock size, shape, and how tightly it compacts. This measurement is fundamental to estimating rock for garden beds and other landscape features.
Why Depth Matters So Much
The depth at which you spread your rock is arguably the most significant factor influencing its coverage. A shallower layer will spread over a larger area, while a thicker layer will cover less ground.
- Shallow Coverage (1 inch): If you opt for a thinner layer, perhaps for a light decorative mulch effect, your cubic yard of rock will go further, potentially covering up to 200 square feet. However, this is often not enough for practical weed suppression or stable ground cover.
- Standard Coverage (2 inches): This is the most common depth for landscape rock coverage. It provides a good balance between visual appeal, weed control, and stability for walkways or patios. As mentioned, expect coverage of around 100 square feet per cubic yard.
- Deep Coverage (3-4 inches): For areas requiring substantial stability, such as driveways or pathways that will see heavy foot traffic or vehicle use, a depth of 3 to 4 inches is recommended. In this scenario, one cubic yard will cover significantly less area, roughly 50-75 square feet.
Material Density and Compaction: The Hidden Variables
Beyond depth, the type of rock itself plays a role. Different rocks have different densities and shapes, which affect how they settle and compact.
- Angular Crushed Stone: Rocks with sharp, angular edges tend to interlock more effectively, creating a stable surface that compacts well. This can sometimes lead to slightly less coverage than expected due to tighter packing.
- Rounded Gravel: Smoother, rounded stones may not interlock as tightly. This can mean they spread out a bit more easily, potentially increasing gravel coverage per yard, but they might also shift more readily.
- Pea Gravel: This is a smaller, rounded gravel. Due to its size, it can sometimes require a slightly deeper layer to achieve the same stability as larger aggregate.
- Decorative River Rock: These are typically larger, rounded stones and are primarily for aesthetic purposes. They don’t compact in the same way as crushed stone and are often used in shallower decorative layers, meaning a cubic yard will cover a larger area.
It’s also important to consider that many rock products will settle and compact after initial spreading, especially after rain or traffic. This means that while your initial spread might look generous, it will likely settle to a slightly more compact state over time. Planning for this initial settling is key to accurate estimating rock for garden beds.
Practical Application: Calculating Your Needs
Now that we have the basic principles, let’s get into the practical side of calculating rock volume for your specific project.
Step 1: Measure Your Area
The first and most critical step is to accurately measure the area you intend to cover.
- Rectangular or Square Areas: Measure the length and width of the space in feet.
- Formula: Area (sq ft) = Length (ft) × Width (ft)
- Circular Areas: Measure the radius (distance from the center to the edge) in feet.
- Formula: Area (sq ft) = π × Radius² (ft²) (where π is approximately 3.14)
- Irregular Areas: Break down the irregular shape into smaller, manageable geometric shapes (rectangles, squares, triangles, circles). Calculate the area of each shape and then sum them up for the total area.
Step 2: Determine Your Desired Depth
Decide on the depth you want for your rock layer. As we’ve discussed, 2 inches is a common standard, but your project might require more or less.
- Convert Inches to Feet: Since most area measurements are in square feet, it’s best to convert your desired depth to feet.
- Formula: Depth (ft) = Depth (in) / 12
Step 3: Calculate Cubic Feet of Rock Needed
Once you have the area in square feet and the depth in feet, you can calculate the total volume of rock needed in cubic feet.
- Formula: Volume (cu ft) = Area (sq ft) × Depth (ft)
Step 4: Convert Cubic Feet to Cubic Yards
Since rock is typically sold by the cubic yard, you’ll need to convert your cubic foot measurement. There are 27 cubic feet in 1 cubic yard.
- Formula: Volume (cu yd) = Volume (cu ft) / 27
Example Calculation
Let’s say you have a garden bed that is 10 feet long and 5 feet wide, and you want to cover it with 3 inches of decorative gravel for weed suppression and a neat appearance.
- Area: 10 ft × 5 ft = 50 sq ft
- Depth: 3 inches / 12 inches/ft = 0.25 ft
- Volume (cu ft): 50 sq ft × 0.25 ft = 12.5 cu ft
- Volume (cu yd): 12.5 cu ft / 27 cu ft/cu yd = 0.46 cu yd
Since you can’t typically buy fractions of a cubic yard and it’s always wise to have a little extra, you would likely round up and purchase 0.5 cubic yards (or 1 cubic yard if purchasing in half-yard increments isn’t possible). This illustrates why how much gravel do I need is a practical calculation.
Using a Rock Yard Coverage Calculator
Many landscaping suppliers and online resources offer rock yard coverage calculator tools. These can be incredibly helpful as they often have pre-set common depths and can factor in the typical compaction rates for different rock types. You simply input your area dimensions and desired depth, and the calculator provides an estimated amount in cubic yards.
How to Use Online Calculators Effectively
- Measure Accurately: The calculator is only as good as the information you put into it. Double-check your measurements.
- Know Your Desired Depth: Be clear about how deep you want the rock to be.
- Consider Rock Type: Some advanced calculators might ask for the type of rock. If not, make a note of it, as it can influence your final quantity.
- Add a Buffer: It’s always a good idea to add 10-15% to your calculated amount to account for settling, uneven spreading, and potential mistakes.
Estimating Rock for Garden Beds: Specific Considerations
Estimating rock for garden beds involves a few nuances. While the general calculations apply, garden beds are often more complex in shape and may have varying depths within the same bed.
Shapes and Edging
Garden beds are rarely perfect rectangles. They can be curved, have irregular edges, or incorporate features like trees or shrubs.
- Measure in Sections: If you have a long, winding garden bed, measure it in several straight sections and add the areas together.
- Account for Obstructions: Don’t include the area directly around the base of large plants or trees where you won’t be spreading rock.
Depth for Different Purposes
- Weed Suppression: For effective weed control, a minimum depth of 2-3 inches is generally recommended.
- Aesthetic Mulch: If you’re using rock purely for decoration, a shallower layer of 1-2 inches might suffice, but ensure it still provides adequate coverage.
- Drainage: In some instances, rock is used for drainage. This might require a deeper layer, potentially 4-6 inches, especially at the base of planters or in areas prone to waterlogging.
Using Ground Cover Fabric
If you plan to use landscape fabric underneath your rock, you’ll still need to calculate the rock volume as usual. The fabric’s purpose is weed suppression and preventing the rock from sinking into the soil, but it doesn’t change the amount of rock needed to achieve a desired depth.
Spreading Landscape Rock: Tips for Efficiency
Once you have your rock, proper spreading landscape rock is key to achieving the desired look and coverage.
Tools of the Trade
- Shovels: Heavy-duty shovels are essential for moving bulk rock.
- Wheelbarrow: A sturdy wheelbarrow is crucial for transporting rock from the delivery point to the spreading area.
- Rakes: Garden rakes, landscape rakes, and landscape leveling rakes are invaluable for distributing and smoothing the rock.
- Measuring Tools: A tape measure will help you check your depth as you go.
Techniques for Even Coverage
- Start in the Center: Begin spreading from the center of your area and work outwards. This helps prevent you from trapping yourself in a corner.
- Work in Small Sections: Don’t try to dump large piles and spread them all at once. Work with manageable amounts to ensure an even distribution.
- Layer by Layer: If you need a deeper layer, spread it in two or more thinner layers, raking and leveling each one before adding the next. This helps achieve a more consistent depth.
- Check Your Depth Frequently: Use your tape measure to check the depth in various spots as you spread. It’s much easier to correct shallow or deep spots as you go than to fix them later.
- Edge with Care: Pay attention to the edges of your area, ensuring the rock doesn’t spill over into unwanted places.
Common Rock Coverage Scenarios
Let’s look at some typical scenarios and the rock coverage area you can expect from one cubic yard.
Scenario 1: Pathway
- Area: 20 feet long x 3 feet wide = 60 sq ft
- Desired Depth: 3 inches (0.25 ft)
- Calculation:
- Volume (cu ft) = 60 sq ft × 0.25 ft = 15 cu ft
- Volume (cu yd) = 15 cu ft / 27 = 0.56 cu yd
- Result: You’ll need slightly more than half a cubic yard. Round up to 0.75 or 1 cubic yard to be safe, especially if the pathway will see heavy use and needs good compaction. This answers how much gravel do I need for a walkway.
Scenario 2: Large Garden Bed
- Area: 15 feet long x 10 feet wide = 150 sq ft
- Desired Depth: 2 inches (0.167 ft)
- Calculation:
- Volume (cu ft) = 150 sq ft × 0.167 ft = 25.05 cu ft
- Volume (cu yd) = 25.05 cu ft / 27 = 0.93 cu yd
- Result: You’ll need just under one cubic yard. It’s highly recommended to purchase 1 cubic yard to ensure complete coverage and account for settling. This is a common gravel coverage per yard query.
Scenario 3: Small Decorative Area
- Area: 8 feet x 8 feet = 64 sq ft
- Desired Depth: 1.5 inches (0.125 ft)
- Calculation:
- Volume (cu ft) = 64 sq ft × 0.125 ft = 8 cu ft
- Volume (cu yd) = 8 cu ft / 27 = 0.3 cu yd
- Result: You’ll need about a third of a cubic yard. If purchasing options are limited to half or full yards, you’d opt for 0.5 cubic yards.
These examples highlight the importance of precise measurements and the flexible nature of rock calculations for landscaping.
Factors Affecting Rock Purchases
When you are ready to buy, keep these points in mind:
Bulk vs. Bagged Rock
- Bulk Delivery: Ordering rock in bulk (by the cubic yard) is almost always more economical for larger projects. Delivery fees are usually a flat rate.
- Bagged Rock: Smaller projects might be more convenient with bagged rock, but the cost per cubic yard is significantly higher. Check the weight and coverage stated on the bag to do your own calculating rock volume comparison. A typical bag of landscape rock weighs around 40-50 lbs and might cover about 0.5 cubic feet.
Rock Size and Type Availability
- Local Suppliers: Prices and availability of specific rock types can vary greatly depending on your location. It’s worth checking with local nurseries, garden centers, and landscape material suppliers.
- Specialty Rocks: Some decorative rocks can be more expensive due to their rarity, color, or origin. This can affect your overall budget, but usually not the fundamental cubic yard rock coverage calculations.
Site Access
Consider how the rock will be delivered. If your property has narrow access roads, large trucks might not be able to reach your desired location, potentially requiring you to accept delivery at a further point and transport it yourself.
FAQs About Rock Coverage
Q1: How much gravel do I need for a 10×10 patio?
For a 10×10 patio (100 sq ft) with a standard 2-inch gravel depth, you will need approximately 1 cubic yard of gravel. This aligns with the general rule of thumb.
Q2: Can I use a thinner layer of gravel for weed control?
While a thinner layer might provide some minimal weed suppression, a depth of at least 2-3 inches is generally recommended for effective weed control. Shallower layers are less effective over time.
Q3: What is the best way to calculate how much rock is needed for a circular garden bed?
Measure the radius of the circular bed (from the center to the edge) in feet. Use the formula: Area = π * radius². Then, convert your desired depth from inches to feet and multiply by the area to get cubic feet. Finally, divide by 27 to get cubic yards.
Q4: Does the type of rock affect how much it covers?
Yes, the shape and size of the rock can influence its density and how it compacts. Angular rocks tend to interlock and compact more tightly than rounded gravel, potentially affecting rock coverage area.
Q5: How much does a cubic yard of rock typically weigh?
The weight of a cubic yard of rock can vary significantly based on its type and moisture content, but it generally ranges from 2,000 to 2,500 pounds (1 to 1.25 tons).
Q6: How do I estimate rock for garden beds with curved edges?
Break the curved area into smaller, manageable geometric shapes like rectangles and semi-circles. Calculate the area of each section and sum them up for a total area before calculating the rock volume. This method aids in accurate estimating rock for garden beds.
Q7: If I order 2 cubic yards of rock, how much area will it cover at a 2-inch depth?
Two cubic yards of rock, spread at a 2-inch depth, will cover approximately 200 square feet (100 sq ft per cubic yard).
By following these guidelines and using the provided formulas, you can confidently estimate and plan your landscaping projects, ensuring you have the right amount of rock for a beautiful and functional outcome. The key is to measure accurately, determine your depth, and always add a small buffer for settling and potential adjustments when spreading landscape rock.
