A yard of concrete typically weighs between 4,000 and 4,500 pounds. This weight can vary based on the concrete’s mix design, specifically the types and amounts of aggregate, cement, and water used.
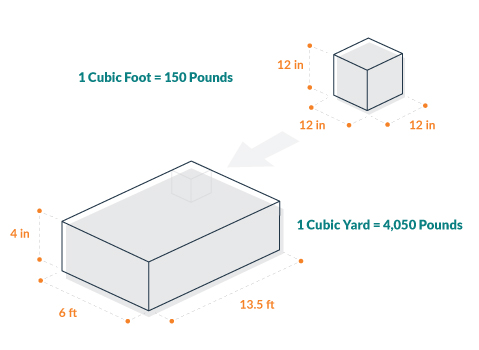
Image Source: www.dumpsters.com
Deciphering Concrete Weight Per Cubic Yard
When embarking on any construction project that involves concrete, a crucial piece of information is the concrete weight per cubic yard. This knowledge is vital for planning, material ordering, transportation, and ensuring the structural integrity of your project. Many people ask, “How much does concrete weigh?” The answer, as we’ve briefly touched upon, isn’t a single fixed number, but rather a range. This article aims to provide a comprehensive exploration of the factors influencing this weight, the typical figures you’ll encounter, and why this information is so important.
Fathoming the Weight of Concrete
The weight of concrete is a fundamental property that directly impacts its application and handling. Whether you’re pouring a small patio or a massive foundation, knowing the density of the material is essential. Concrete is a composite material, meaning it’s made up of several different components. Each of these components contributes to the overall weight.
Concrete Density: The Key Factor
The primary determinant of concrete density is its mix design. Concrete is primarily composed of:
- Aggregates: These are granular materials like sand, gravel, and crushed stone. They make up the largest portion of the concrete mix by volume and weight. The type, size, and specific gravity of the aggregate significantly influence the final density. Denser aggregates will result in heavier concrete.
- Cement: This is the binder that holds everything together. Portland cement is the most common type. While it contributes to weight, its proportion in the mix is typically less than that of aggregates.
- Water: Water is essential for the chemical reaction (hydration) that hardens the cement. The water-to-cement ratio affects both strength and weight.
Typical Concrete Weight in Pounds Per Cubic Yard
For standard structural concrete, you can expect the pounds per cubic yard concrete to fall within a predictable range.
Standard Concrete Mixes
A typical concrete mix, designed for general-purpose use like sidewalks, driveways, and basic foundations, generally weighs around 4,000 to 4,150 pounds per cubic yard. This is a good baseline figure for most common construction tasks.
High-Strength Concrete
Concrete mixes designed for higher strength, often used in structural elements like beams, columns, and high-rise buildings, may contain denser aggregates or a higher cement content. This can push the cubic yard concrete weight upwards, sometimes reaching 4,300 to 4,500 pounds per cubic yard or even more.
Lightweight Concrete
Conversely, lightweight concrete uses special lightweight aggregates, such as expanded shale, clay, or slate. These mixes are significantly lighter, with weights ranging from 100 to 120 pounds per cubic foot, translating to roughly 2,700 to 3,240 pounds per cubic yard. This type of concrete is used when reducing the overall structural load is critical, such as in precast floor slabs or insulating layers.
Translating Concrete Volume to Weight
The conversion from concrete volume to weight is a straightforward calculation once you have the density. The formula is simple:
Weight = Volume × Density
If you know the density in pounds per cubic yard and the volume in cubic yards, the calculation is direct.
Example Calculation
Let’s say you need to pour a concrete patio that measures 10 feet long by 10 feet wide and 4 inches thick.
-
Calculate the Volume in Cubic Feet:
- Length = 10 ft
- Width = 10 ft
- Thickness = 4 inches = 4/12 feet = 0.333 ft
- Volume (cu ft) = 10 ft × 10 ft × 0.333 ft = 33.3 cubic feet
-
Convert Cubic Feet to Cubic Yards:
- There are 27 cubic feet in 1 cubic yard (3 ft × 3 ft × 3 ft = 27 cu ft).
- Volume (cu yd) = 33.3 cu ft / 27 cu ft/cu yd = 1.23 cubic yards
-
Calculate the Weight (using a typical density of 4,100 lbs/cu yd):
- Weight = 1.23 cu yd × 4,100 lbs/cu yd = 5,043 pounds
So, for this patio, you would need approximately 5,043 pounds of concrete. It’s always advisable to order slightly more than your calculated amount to account for waste, spillage, and uneven subgrade.
Factors Influencing Concrete Weight
While the general figures are helpful, several factors can cause the concrete weight to fluctuate:
Aggregate Type and Size
- Type: The specific gravity of the aggregate is a major influencer. For example, granite and basalt are denser than limestone or sandstone. Using denser aggregates will increase the concrete density.
- Size: Larger aggregate particles generally leave more voids within the concrete mix. However, the material itself is often denser, and the overall effect on weight per cubic yard is complex and dependent on the specific mix. The weight of concrete is intricately tied to the materials used to make it.
Water-to-Cement Ratio (w/c Ratio)
A lower w/c ratio generally leads to denser, stronger concrete, which can also mean it’s slightly heavier per cubic yard. Conversely, a higher water content, often used for easier workability, can slightly decrease the density if not compensated for by other mix components.
Admixtures
Chemical admixtures are added to concrete to modify its properties.
- Air-entraining agents: These create tiny air bubbles in the concrete, which improves freeze-thaw resistance but slightly reduces the concrete weight per cubic yard.
- Superplasticizers: These allow for a lower water content while maintaining workability, potentially leading to denser and slightly heavier concrete.
Reinforcement (Steel Rebar)
While this article focuses on the weight of the concrete itself, it’s important to note that reinforced concrete will weigh more. Steel rebar is significantly denser than concrete. A cubic yard of concrete with a typical amount of rebar will therefore weigh more than a cubic yard of plain concrete.
Why Knowing Concrete Weight Matters
Accurate knowledge of how much does concrete weigh is not just for academic interest; it has practical implications for construction projects:
Structural Load Calculations
Engineers need to know the weight of concrete to calculate the total load on foundations, columns, and beams. This is critical for the stability and safety of any structure. A heavier concrete slab will exert more pressure on the supporting structure below it.
Transportation and Logistics
Concrete is typically transported in concrete truck capacity units, which are measured in cubic yards. Knowing the weight per cubic yard is essential for:
- Truck Load Limits: Ensuring you don’t overload trucks, which is a safety and legal concern.
- Delivery Scheduling: Understanding how much material can be safely transported in a single trip.
- Cost Estimation: Transportation costs can sometimes be influenced by weight.
Material Ordering
When ordering concrete from a ready-mix plant, you’ll specify the volume in cubic yards. However, understanding the weight helps in communicating with suppliers and ensuring you’re ordering the appropriate mix for your needs.
Project Budgeting
The cost of concrete can sometimes be influenced by the density of the mix and the aggregates used. Knowing the expected weight can aid in more accurate budgeting.
Common Concrete Applications and Their Weight Considerations
Let’s look at some common construction elements and how their weight of concrete considerations play a role:
Concrete Slab Weight
The concrete slab weight is a significant factor in building design.
- Foundations: Slabs-on-grade for houses typically use a standard mix. The weight of these slabs needs to be accounted for in the foundation design to prevent settling or cracking.
- Floors: In multi-story buildings, floor slabs are a major contributor to the building’s overall weight. Engineers carefully select concrete mixes to balance strength, weight, and cost. Lightweight concrete is often used in upper floors to reduce the load on lower levels and the foundation.
- Patios and Sidewalks: For these applications, the exact weight is less critical from a structural load perspective but still important for ordering and transport.
Driveways and Walkways
A typical residential driveway might be 4 inches thick. A standard 10×20 foot driveway would require approximately 2.5 cubic yards of concrete. At 4,100 lbs/cu yd, this amounts to over 10,000 pounds of material.
Retaining Walls
The weight of concrete is crucial for the stability of retaining walls. The sheer mass of the concrete helps resist the lateral pressure exerted by the soil behind it. The concrete density is a key factor in the wall’s ability to stand firm.
Calculating Concrete Volume for Projects
Accurate measurement of your project’s concrete volume to weight is paramount. Always measure the dimensions of your pour area carefully.
Key Steps for Volume Calculation:
- Measure Length, Width, and Depth: Ensure all measurements are in the same units (feet are most common).
- Convert Depth to Feet: If depth is in inches, divide by 12.
- Multiply Dimensions: Length × Width × Depth = Volume in cubic feet.
- Convert to Cubic Yards: Divide the cubic feet by 27.
Example: A rectangular footing that is 3 feet wide, 1 foot deep, and 20 feet long.
* Volume (cu ft) = 3 ft × 1 ft × 20 ft = 60 cu ft
* Volume (cu yd) = 60 cu ft / 27 cu ft/cu yd = 2.22 cu yd
For irregularly shaped areas, break them down into simpler geometric shapes (rectangles, triangles, circles) and sum their volumes.
Understanding the Concrete Mix Components in Detail
Let’s delve a bit deeper into how each component impacts the weight of concrete:
Aggregates: The Heavy Lifters
Aggregates typically make up 60-75% of the concrete mix by volume and 70-80% by weight.
- Sand (Fine Aggregate): Typically has a specific gravity of around 2.65.
- Gravel/Crushed Stone (Coarse Aggregate): Specific gravity can range from 2.6 to 2.8 or higher, depending on the rock type.
The higher the specific gravity of the aggregates, the denser and heavier the resulting concrete will be. For instance, using a dense granite aggregate will yield heavier concrete than using a lighter limestone.
Cement: The Binder
Portland cement has a specific gravity of approximately 3.15. While denser than most aggregates, its proportion in the mix is lower, so its impact on the overall concrete density is less pronounced than that of aggregates.
Water: The Reactant
Water has a specific gravity of 1.0. Its contribution to the total weight is relatively small, but the amount of water used (w/c ratio) is crucial for strength and can indirectly affect the final density.
Specialized Concrete Weights
Beyond standard concrete, other types have distinct weight characteristics:
Reinforced Concrete
When steel reinforcing bars (rebar) are added, the weight of concrete increases significantly. Steel has a density of approximately 490 pounds per cubic foot, which is about 7.8 times denser than water and considerably denser than typical concrete. A cubic yard of concrete with a typical amount of rebar can weigh anywhere from 4,500 to over 5,000 pounds.
Precast Concrete
Precast concrete elements, like beams, pipes, or wall panels, are made in a factory. The mix designs can be optimized for specific applications, sometimes leading to higher densities and weights due to the controlled curing and mix proportions.
The Role of the Concrete Truck
Concrete truck capacity is usually measured in cubic yards, with standard mixer trucks holding between 8 and 11 cubic yards of freshly mixed concrete. However, they rarely carry their maximum capacity for practical reasons, often topping out around 9 cubic yards for a full load.
When a full 9-yard load of standard concrete is transported, the truck is carrying approximately:
- 9 cu yd × 4,100 lbs/cu yd = 36,900 pounds (about 18.5 tons) of concrete alone.
This significant weight, plus the weight of the truck itself, highlights why load capacities and road regulations are important.
FAQs About Concrete Weight
Here are some common questions people have about how much concrete weighs:
Q1: What is the average weight of concrete per cubic yard?
A1: The average weight of concrete is typically between 4,000 and 4,500 pounds per cubic yard for standard structural concrete.
Q2: How much does a concrete slab weigh?
A2: The weight of a concrete slab depends on its thickness, dimensions, and the specific concrete mix used. A general estimate can be made by calculating the volume in cubic yards and multiplying by the density per cubic yard.
Q3: Can I estimate the weight of concrete myself?
A3: Yes, by knowing the volume of concrete you need (in cubic yards) and the typical density of the concrete mix (e.g., 4,100 lbs/cu yd), you can calculate the estimated weight.
Q4: Why is the weight of concrete important for construction?
A4: It’s crucial for structural load calculations, ensuring foundations and supporting structures can bear the weight. It also impacts transportation logistics and material ordering.
Q5: Does the type of aggregate change the weight of concrete?
A5: Yes, the type and specific gravity of aggregates are primary factors influencing concrete density and thus its weight per cubic yard. Denser aggregates lead to heavier concrete.
Q6: How does the amount of water affect concrete weight?
A6: While water is a small component by weight, the water-to-cement ratio can influence the final density. Lower water-cement ratios often result in denser, stronger, and slightly heavier concrete.
Q7: What is the typical weight of lightweight concrete?
A7: Lightweight concrete typically weighs between 2,700 and 3,240 pounds per cubic yard, significantly less than standard concrete.
Q8: How much does a cubic yard of concrete weigh if it has rebar?
A8: Reinforced concrete will weigh more than plain concrete. The addition of steel rebar can increase the weight to 4,500 pounds per cubic yard or more.
Q9: What is the weight of concrete in a standard concrete truck?
A9: A standard concrete truck typically carries around 9 cubic yards. At an average density of 4,100 lbs/cu yd, this is approximately 36,900 pounds or 18.5 tons of concrete.
Q10: Are there resources to find specific concrete densities?
A10: Yes, concrete suppliers and mix design guides will often provide the density of their specific concrete mixes, which is helpful for accurate calculations.
Conclusion
The question of “how much does concrete weigh” leads us into the fascinating world of material science and construction. The concrete weight per cubic yard is not a static number but a range influenced by a precise interplay of aggregates, cement, water, and admixtures. Typically falling between 4,000 and 4,500 pounds per cubic yard for standard mixes, this property dictates crucial aspects of project planning, engineering, and logistics. By grasping the factors that contribute to concrete density and understanding how to accurately calculate concrete volume to weight, you can ensure your projects are built safely, efficiently, and soundly. Whether you’re a seasoned contractor or a DIY enthusiast, this knowledge is a cornerstone of successful concrete work.
